
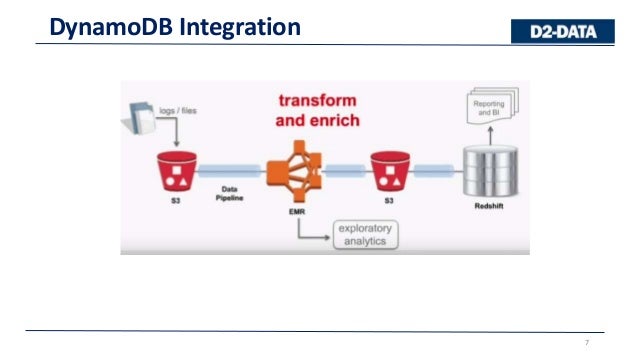
 Scalability: When customers want to scale their traditional on-premise data warehouses, it means more hardware if process and storage demands increase. So, when it comes to performance, Redshift leaves traditional data warehouses in the dust. Performance: Redshift handles data processing and queries with lightning speed, thanks to its massively parallel processing (MPP) and columnar data storage configuration. On the other hand, Redshift is a cost-effective, fully-managed solution that imposes no onerous startup or maintenance costs. The charges start with a substantial outlay for hardware, then hiring dedicated personnel to operate the machinery. Cost: The traditional data warehouse model comes with a hefty price tag. Now let’s see how Amazon Redshift compares to conventional data warehouses, breaking down the faceoff into four key areas. Here’s a chart showing the layout, courtesy Amazon AWS.Īmazon Redshift vs. The database contains seven tables, consisting of two fact tables and five dimensions. This sample database is called TICKIT, and its dataset can be loaded by consulting the Amazon Redshift Getting Started Guide. What Is AWS Redshift: AWS Redshift Database Example It's also called an OLAP-style (Online Analytical Processing) database. Redshift is a fully managed data warehouse, giving users the capacity, to begin with, a few gigabytes of data and eventually scale it to petabytes. In addition, it's a column-oriented database, so it stores data in a columnar format that boosts the performance when it reads and writes data. Although Redshift is an analytics database, it's flexible enough to allow cloud users to run traditional relational databases. Each cluster runs its Redshift engine and holds at least one database. Redshift employs massively parallel processing (MPP) technology, so it can process vast amounts of data at fantastic speeds and is very cost-effective in the process.Įvery Amazon Redshift data warehouse includes a set of nodes organized into a cluster. If you want to answer the question “what is AWS Redshift,” where better to go than the host’s website? According to Amazon AWS, AWS Redshift is “…a fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service in the cloud.” So, if you’re looking for a resource to help your organization or business handle the terabytes of new data generated daily, you have come to the right place.Īmazon's warehouse product is perfect for large-scale data analysis and storage, as well as large-scale database migrations. These vast numbers paint a vivid picture of how much data there is out there. A petabyte equals one million gigabytes (roughly 1,024 terabytes). If you’re going to delve into the subject of massive data amounts, you should become familiar with these more exotic data byte measurement terms. What’s a Terabyte and How Does It Compare With an Exabyte? We will answer the question: “what is AWS Redshift”, how it differs from traditional warehouses, its benefits and limitations, Redshift pricing, and setting up a Redshift database. That's why we're focusing today on AWS Redshift.
Scalability: When customers want to scale their traditional on-premise data warehouses, it means more hardware if process and storage demands increase. So, when it comes to performance, Redshift leaves traditional data warehouses in the dust. Performance: Redshift handles data processing and queries with lightning speed, thanks to its massively parallel processing (MPP) and columnar data storage configuration. On the other hand, Redshift is a cost-effective, fully-managed solution that imposes no onerous startup or maintenance costs. The charges start with a substantial outlay for hardware, then hiring dedicated personnel to operate the machinery. Cost: The traditional data warehouse model comes with a hefty price tag. Now let’s see how Amazon Redshift compares to conventional data warehouses, breaking down the faceoff into four key areas. Here’s a chart showing the layout, courtesy Amazon AWS.Īmazon Redshift vs. The database contains seven tables, consisting of two fact tables and five dimensions. This sample database is called TICKIT, and its dataset can be loaded by consulting the Amazon Redshift Getting Started Guide. What Is AWS Redshift: AWS Redshift Database Example It's also called an OLAP-style (Online Analytical Processing) database. Redshift is a fully managed data warehouse, giving users the capacity, to begin with, a few gigabytes of data and eventually scale it to petabytes. In addition, it's a column-oriented database, so it stores data in a columnar format that boosts the performance when it reads and writes data. Although Redshift is an analytics database, it's flexible enough to allow cloud users to run traditional relational databases. Each cluster runs its Redshift engine and holds at least one database. Redshift employs massively parallel processing (MPP) technology, so it can process vast amounts of data at fantastic speeds and is very cost-effective in the process.Įvery Amazon Redshift data warehouse includes a set of nodes organized into a cluster. If you want to answer the question “what is AWS Redshift,” where better to go than the host’s website? According to Amazon AWS, AWS Redshift is “…a fully managed, petabyte-scale data warehouse service in the cloud.” So, if you’re looking for a resource to help your organization or business handle the terabytes of new data generated daily, you have come to the right place.Īmazon's warehouse product is perfect for large-scale data analysis and storage, as well as large-scale database migrations. These vast numbers paint a vivid picture of how much data there is out there. A petabyte equals one million gigabytes (roughly 1,024 terabytes). If you’re going to delve into the subject of massive data amounts, you should become familiar with these more exotic data byte measurement terms. What’s a Terabyte and How Does It Compare With an Exabyte? We will answer the question: “what is AWS Redshift”, how it differs from traditional warehouses, its benefits and limitations, Redshift pricing, and setting up a Redshift database. That's why we're focusing today on AWS Redshift. 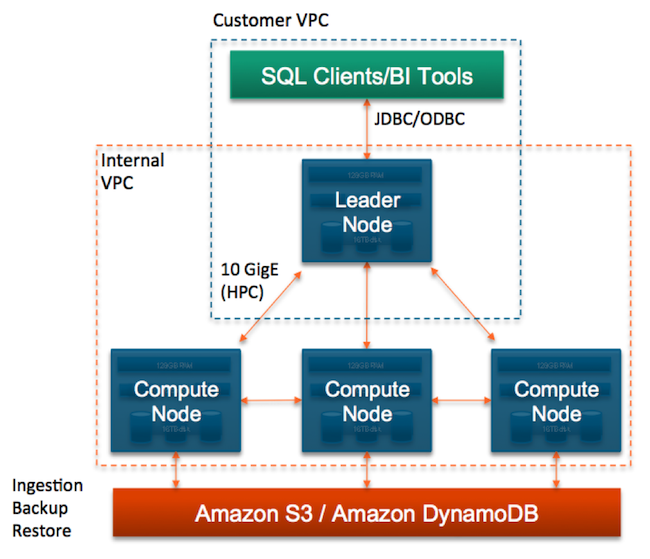
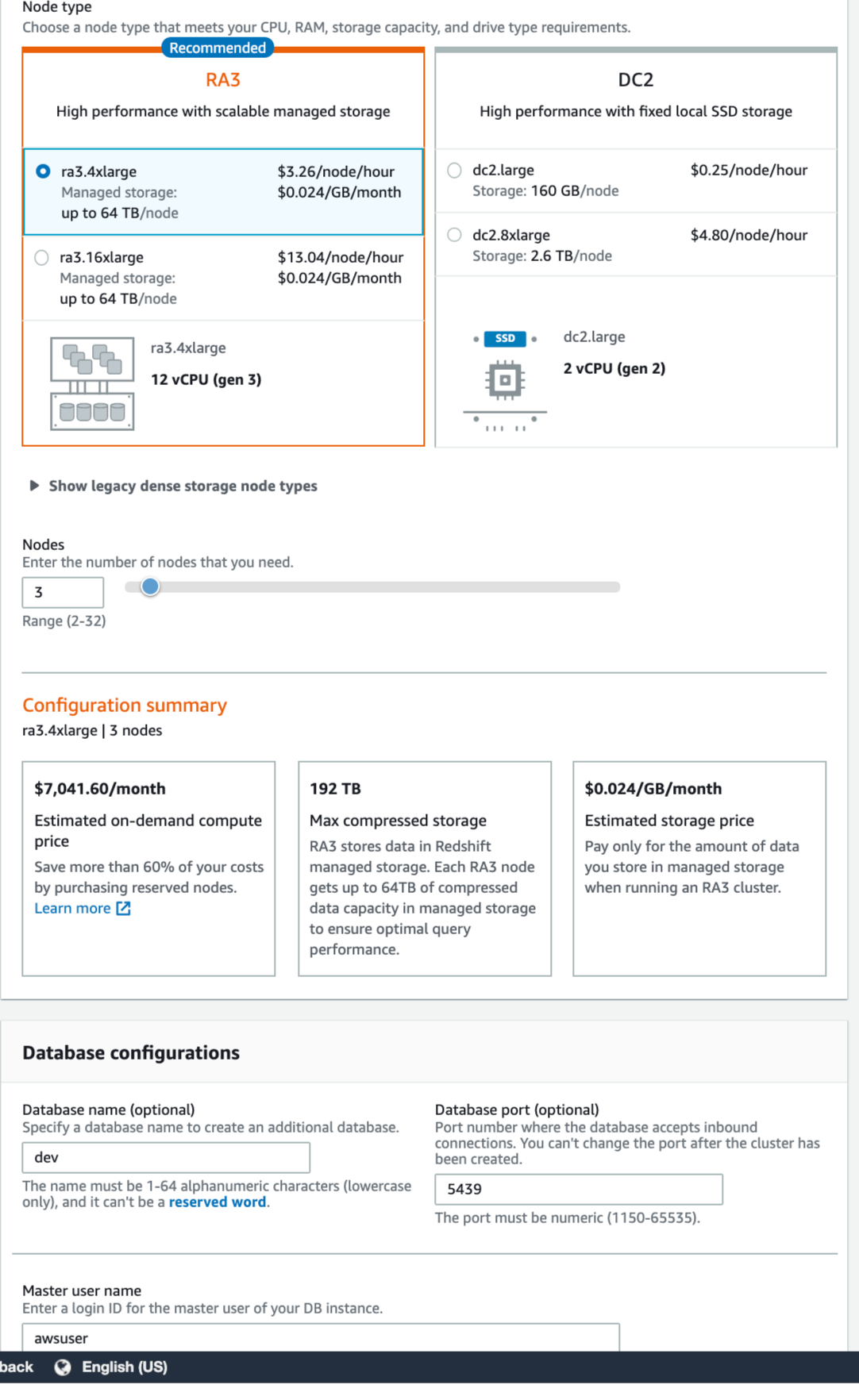
So how can organizations work with exabytes of data and separate the wheat from the chaff? With a colossally sized data warehouse, of course. In these challenging, competitive times, firms enjoy a decreased margin for error when they have the correct data to back up their strategies, which could be a difference-maker.īut there's so much data, and a significant amount of it isn't even helpful to businesses.

Data-driven decisions are informed decisions and have a greater chance of success. Today's businesses use data to make critical decisions. Presenting the understatement of the day: “That is a lot of data!” And that’s not just from human sources-in 2020, machine-generated raw data made up 40% of online data. Welcome to the Information Age, where we create 2.5 quintillion bytes (also known as exabytes) of data every day.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
